What Jobs Will Replace?
Check your career opportunities

Tech Career Quiz: What Tech Job Is Right for You

How to Start a Tech Career with No Experience

The Best Entry-Level Tech Jobs Safe from AI
What jobs will AI replace?
AI's coming for jobs built on routine tasks and repetitive information work. Administration, manufacturing, transportation, customer service—these are the most vulnerable sectors. McKinsey put out a report in 2024 saying 30% of tasks in these areas could be automated by 2030, cutting costs by 40-60% through speed and accuracy gains.
The technology doing this includes machine learning, robotics, and natural language processing. Data entry is already moving to RPA platforms like UiPath and Automation Anywhere—they churn through massive datasets without getting tired or making typos. JPMorgan's CEO Jamie Dimon said in 2025 that the bank had already automated 20% of its back-office positions. Manufacturing's been hit hard too. AI-powered robots now weld, inspect, and assemble with precision humans can't match. The U.S. has lost 5.5 million manufacturing jobs since 2000.
Transportation's next. Goldman Sachs thinks 40% of trucking and delivery jobs—about 3.5 million people in the U.S.—could disappear by 2035. Retail's shifting to self-checkout and chatbots. Generative AI tools like ChatGPT and Jasper are cranking out marketing copy and translations. A 2024 Pew study warned that 30% of entry-level creative roles might vanish by 2035.
But here's the thing: this isn't just doom and gloom. BlackRock's Larry Fink argues AI is "restructuring, not eliminating" jobs. The World Economic Forum found in 2025 that 83% of companies now prioritize AI skills in their hiring. Managing the risk comes down to adapting and learning new skills—figuring out how to work with AI instead of getting replaced by it.
Jobs that AI can't replace
Creative and strategic roles
AI's good at a lot of things, but it can't dream up something genuinely new. It doesn't have intuition or emotional depth. That's why creative and strategic jobs are safer from automation—they run on imagination, cultural awareness, and vision. No algorithm can lead with those. Technology can help, sure. But it can't do the actual creating. Artists find new ways to express ideas. Strategists build brand stories that feel real. Entrepreneurs spot gaps in the market that nobody else noticed. That takes human insight.
Jobs in this category: writers and content creators, graphic designers and artists, marketing strategists and brand managers, film directors and producers, entrepreneurs and business innovators.
AI might make these professionals faster, but the core work—original thinking, big-picture strategy, emotional resonance—stays human.
Interpersonal and empathetic professions
Jobs that need emotional intelligence and real human connection are hard for AI to touch. These roles depend on trust, emotional awareness, and reading complex social situations. AI can spit out scripted responses, but it doesn't actually feel or understand emotions.
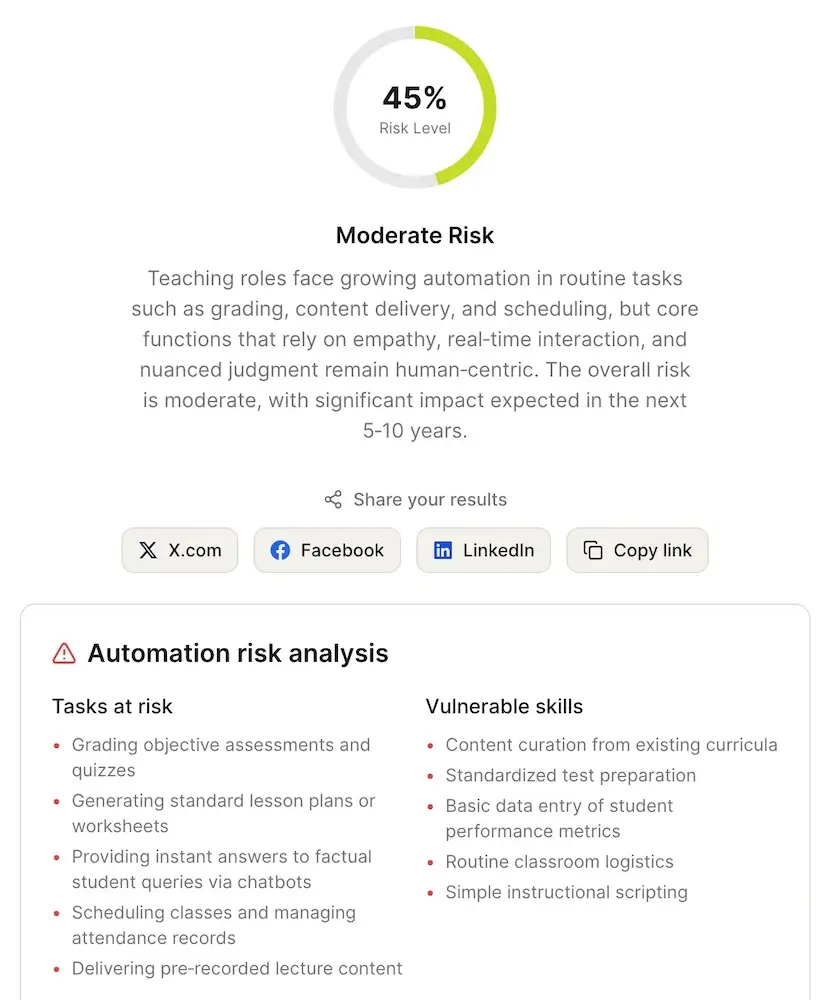
Jobs in this category: psychologists and therapists, nurses and doctors, teachers and educators, social workers and coaches, HR managers and recruiters, sales representatives.
Human connection isn't a nice-to-have in these fields—it's the job. Therapists pick up on tone, facial expressions, things people don't say out loud. Teachers motivate kids and respond to their emotional states in real time. No AI system can genuinely replicate that kind of adaptive, empathetic engagement.
Skilled trades and complex manual work
AI struggles in hands-on, unpredictable situations that need quick thinking and on-the-spot problem-solving. Skilled trades require practical know-how, physical skill, and the ability to adapt as things change—all tough to automate. Robots do fine with repetitive factory work, but throw them onto a construction site or into an emergency repair, and they're lost.
Jobs in this category: electricians and plumbers, carpenters and builders, chefs and culinary experts, mechanics and technicians, emergency responders and firefighters.
These jobs need human judgment and hands-on skill, often in situations that keep changing. A plumber tracking down a hidden leak uses instinct and experience, not just a checklist. A firefighter making split-second decisions in the field draws on training and gut feeling that no machine has. That's why these roles stay with humans.
Why jobs are at risk of AI automation
How our AI job risk calculator works
You're not alone. Nearly half of today's jobs face potential disruption from AI, but understanding your risk level is the first step toward staying ahead.
Take control of your career. Get your AI risk assessment with actionable insights in under 30 seconds.
Analyze your job riskGet your guide to AI-proofing your career



FAQ
What jobs cannot be replaced by AI?
What jobs cannot be replaced by AI?
Healthcare struggles with AI because there's not enough data to share. Only about 10% of medical information is available publicly. Privacy laws like HIPAA keep patient records locked up, and the data sits spread out across different hospitals, insurance companies, and doctors' offices. AI can't learn properly when all the information is trapped in separate places.
Construction is surprisingly safe from AI takeover. It's not because the work is too hard—it's because nobody keeps good digital records. Every building project is different, almost nothing gets documented properly, and there's no consistent way to track what actually works.
Education can't fully use AI because of privacy rules. The U.S. Department of Education points out that laws like FERPA make it hard to collect and share student information. Without access to this data, AI systems can't learn how to help students better.
What jobs will be gone by 2030?
What jobs will be gone by 2030?
Many routine administrative tasks, basic data entry positions, simple customer service roles, and repetitive manufacturing jobs face the highest risk. However, rather than experiencing complete elimination, most jobs will evolve to work alongside AI technology.
How accurate is the job automation risk assessment?
How accurate is the job automation risk assessment?
Our tool analyzes current automation trends, industry reports, and technological developments to provide realistic risk estimates. While we can't predict the future with certainty, the calculator draws from extensive labor market research to give you data-driven insights about potential changes in your field.
What career guidance will I receive?
What career guidance will I receive?
Your report includes an automation risk score from 0-100%, which job tasks face the highest risk, skills worth protecting and developing, a practical action plan with suggested timelines, and alternative career options showing growth potential, typical salaries, and automation risk levels.
What jobs will boom in 2025?
What jobs will boom in 2025?
The big winners are AI-related jobs—machine learning engineers, data scientists, and AI ethicists. Demand for those is going through the roof.
Then there's a whole new category popping up: roles that bridge the gap between humans and AI. Think human-AI collaboration specialists or digital transformation consultants. These didn't really exist five years ago, and now companies are scrambling to hire them.
What industries are most affected by AI?
What industries are most affected by AI?
Manufacturing, retail, transportation, and financial services are getting hit the hardest by AI right now. But here's what's actually happening: most jobs aren't disappearing—they're changing. People are working with AI tools, not getting replaced by them.